Overview
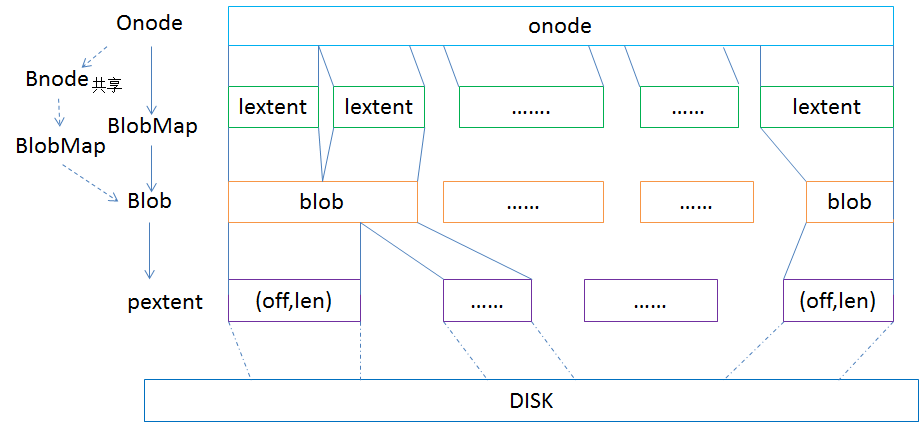 |
|---|
| BlueStore metadata |
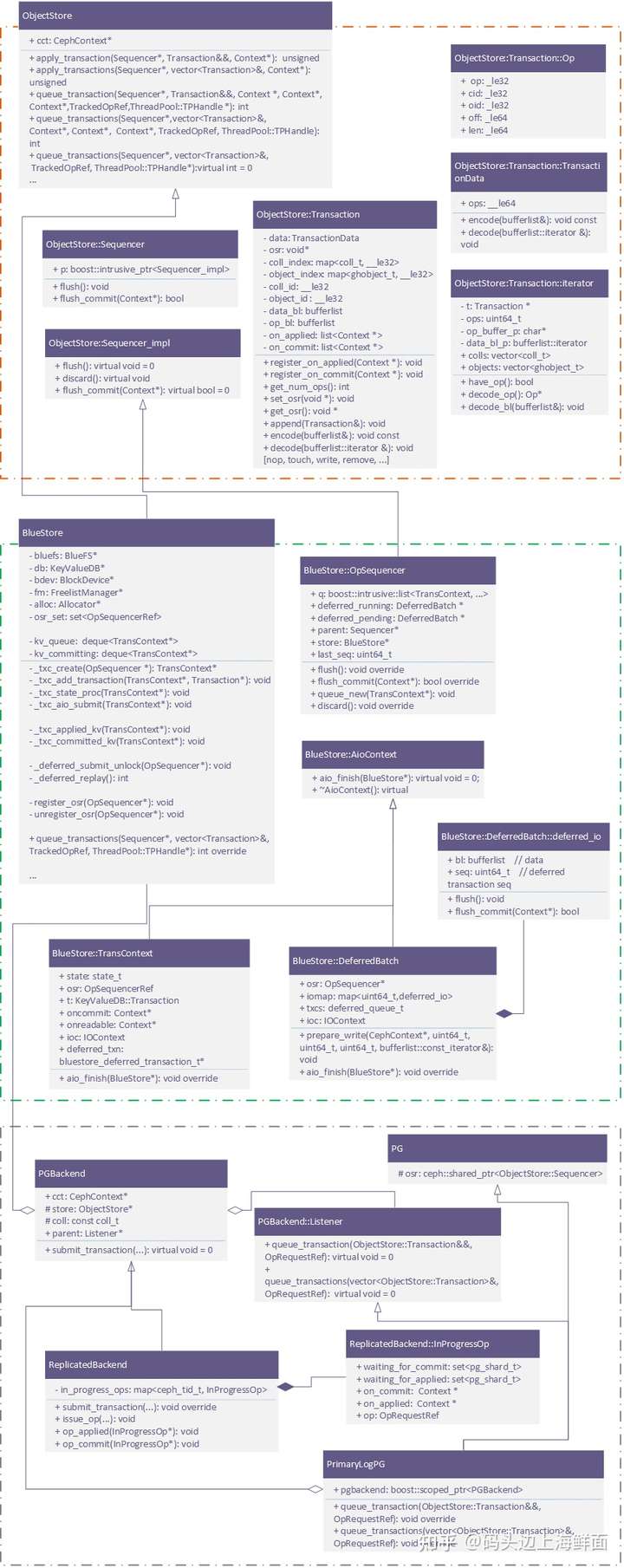 |
|---|
| BlueStore transaction |
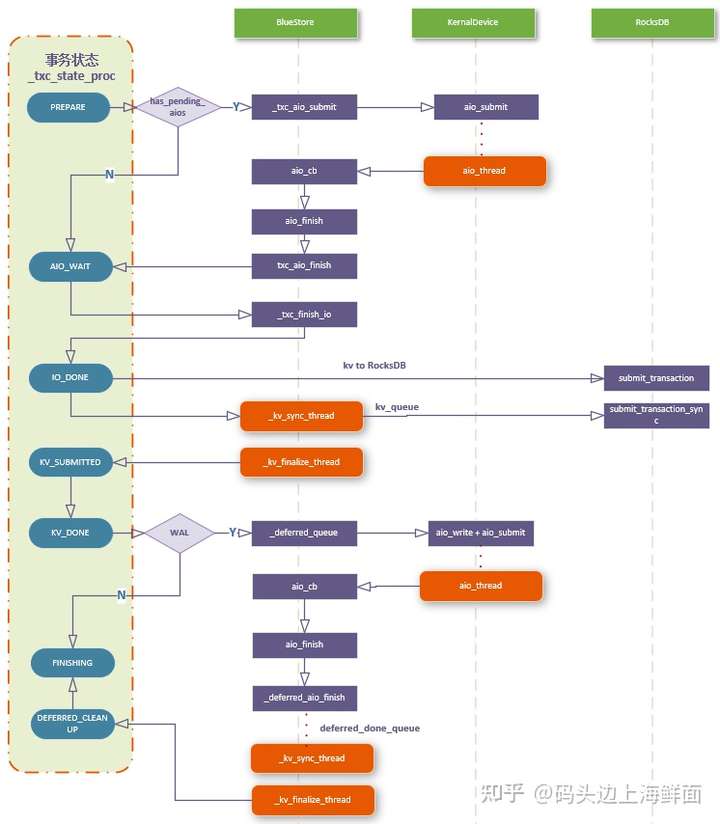 |
|---|
| BlueStore state machine |
Operations
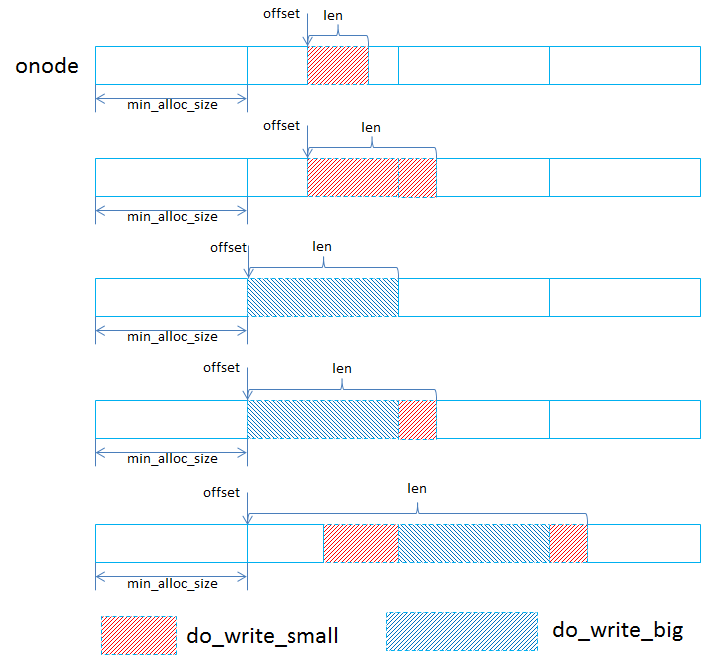
OP_WRITE
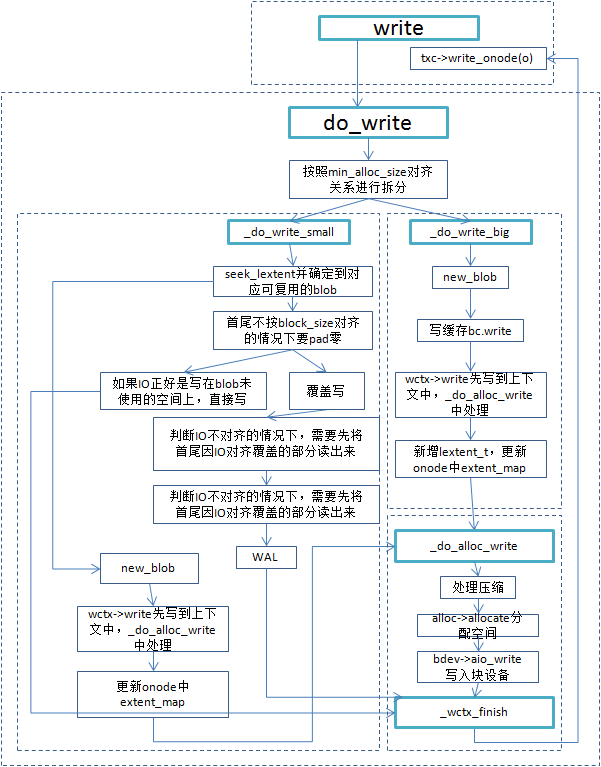 |
|---|
| Write procedure |
 |
|---|
| Write modes |
src/os/bluestore/BlueStore.cc/BlueStore::_do_write_data()
Allocator
StupidAllocator
allocate() repeated calls allocate_int(), until allocated size reaches
wanted size.
src/os/bluestore/StupidAllocator.cc/StupidAllocator::allocate_int()
To understand how StupidAllocator works, the private member
std::vector<ceph::interval_set<
/*offset/length type*/uint64_t,
/*map impl*/btree_map<uint64_t/*offset*/, uint64_t/*length*/>
>> free;
must be explained:
free list, as the name suggests, keeps track of available segments. The vector
is indexed by magnitude of segment size, that is free[0] will be available
segments of [0, 1) block size (bdev_block_size) and free[3] will be of
[4, 8) bs segments. Since interval_set is an
AssociativeContainer,
the segments in a free list entry is naturally sorted by offset.
The number of entries in
freeis fixed to 10 on initialization, i.e. the maximum contiguous managed allocation block size isbdev_block_size << 9.
btree_map_tis likestd::map, but implemented with B-Tree, rather than red-black tree, for smaller footprint.
StupidAllocator then acts as a buddy allocator:
-
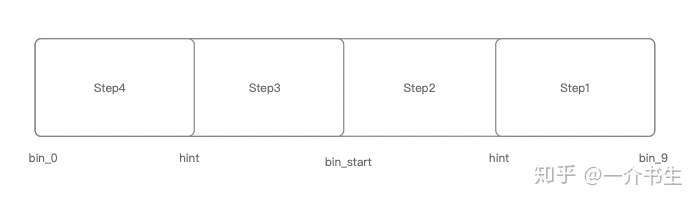
_choose_bin()- returns a chosen binorig_binfrom available segmentsGiven target allocation size
len, returns the minimum among effective bits oflenand the last element offreelist.PERF: Implemented with
__builtin_clz(ll)Count Leading Zero instruction. - For segments no smaller than
orig_bins, i.e. entries after and includingfree[orig_bin], search heuristically fromhintaddress.The default hint is the immediate address after last allocation.
- For segments no smaller than
orig_bins, search from lowest address (up tohint, because already searched). - For segments smaller than
orig_bins, xxxxAllocate something at least.
 |
|---|
Heuristic search range and its order (bin_start is orig_bin) |
- Manage
free.